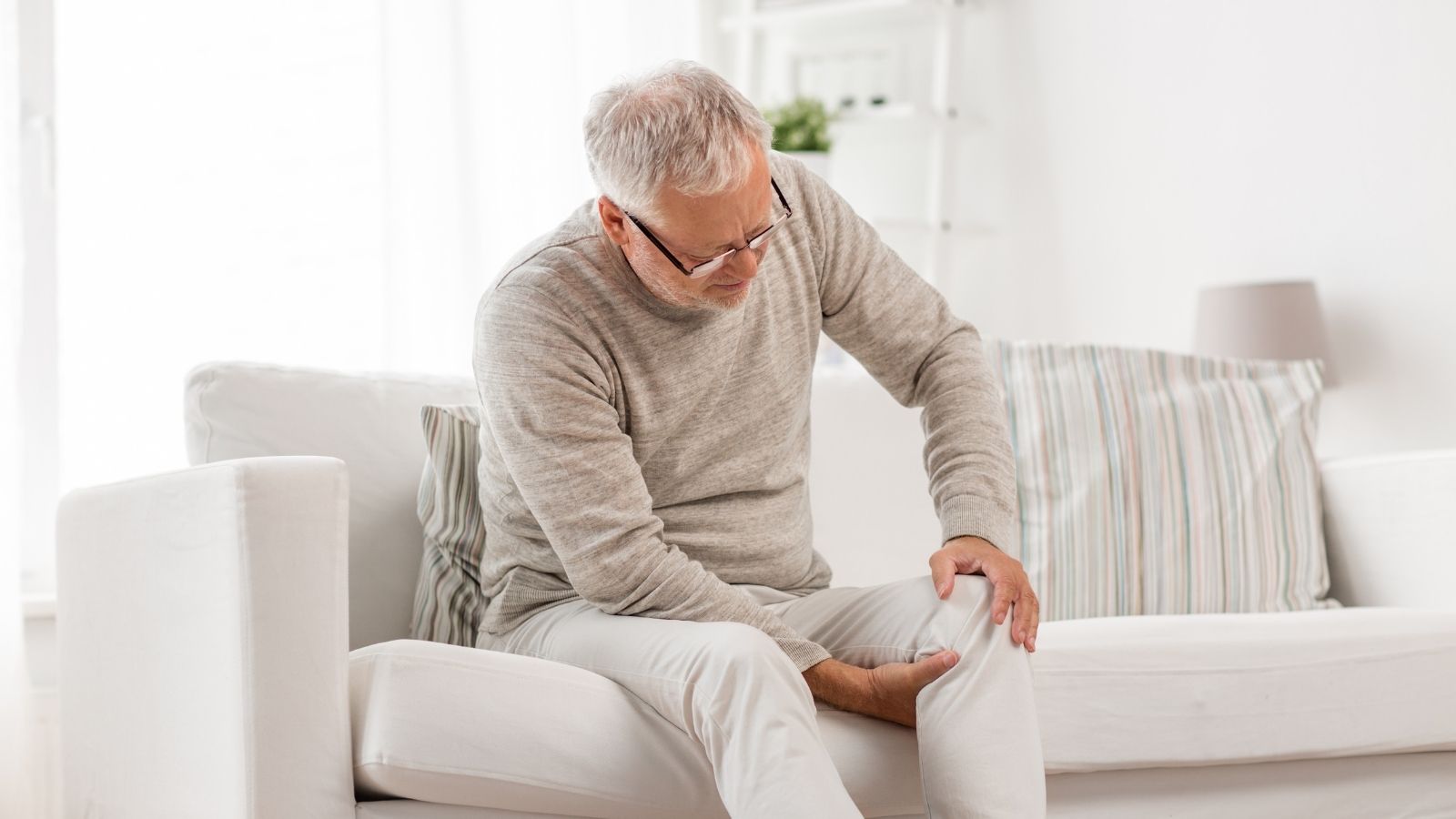
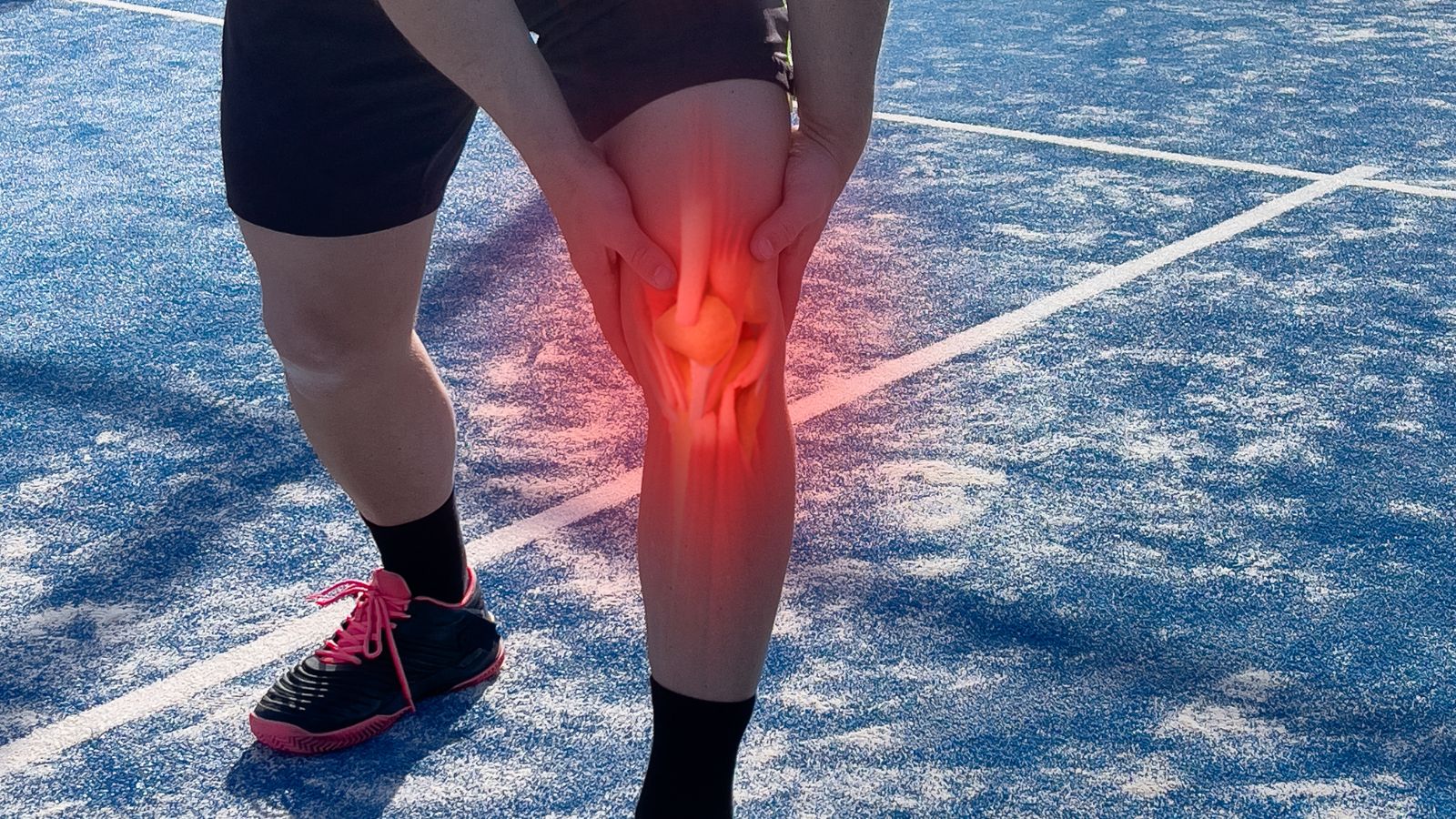
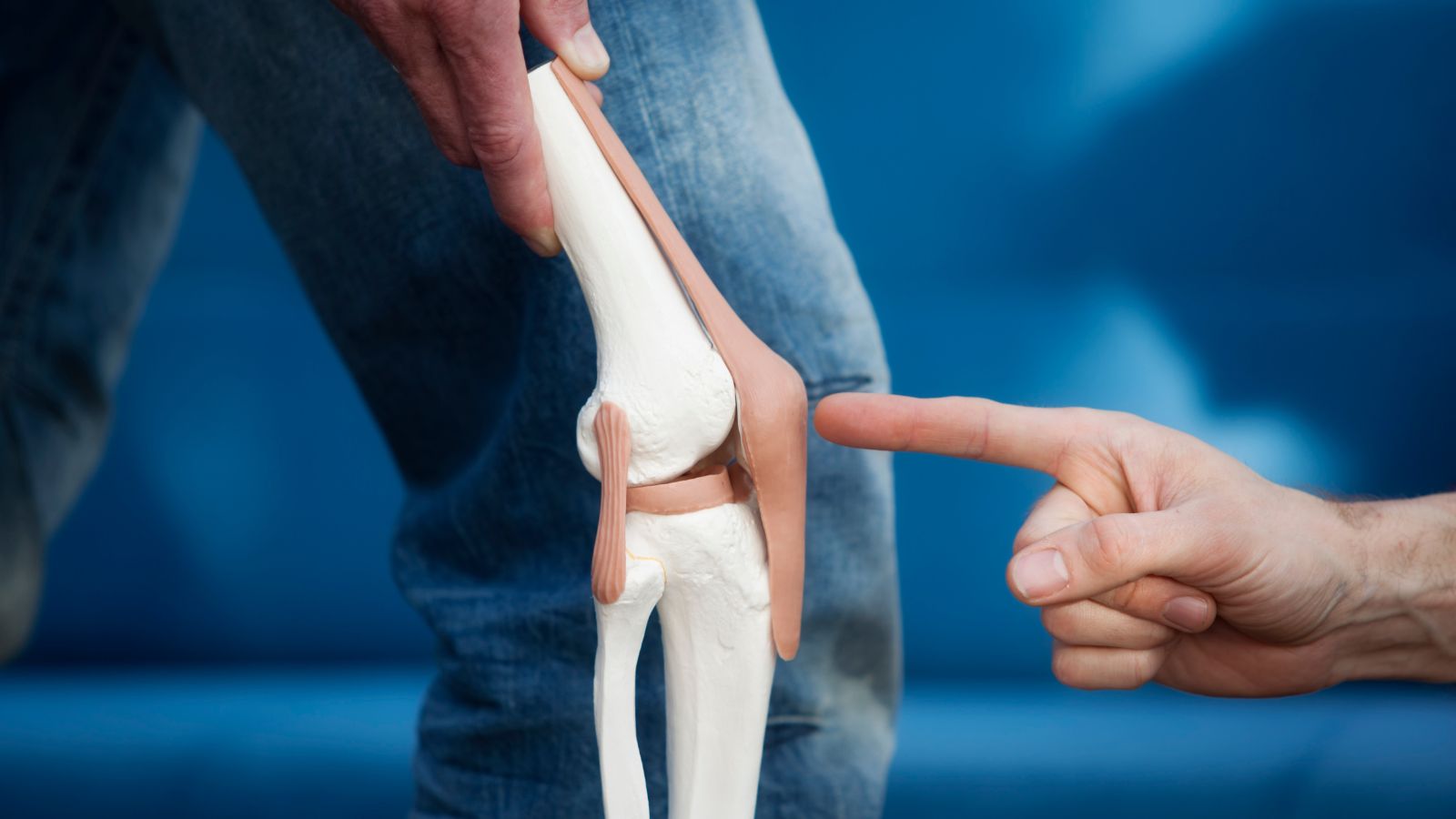
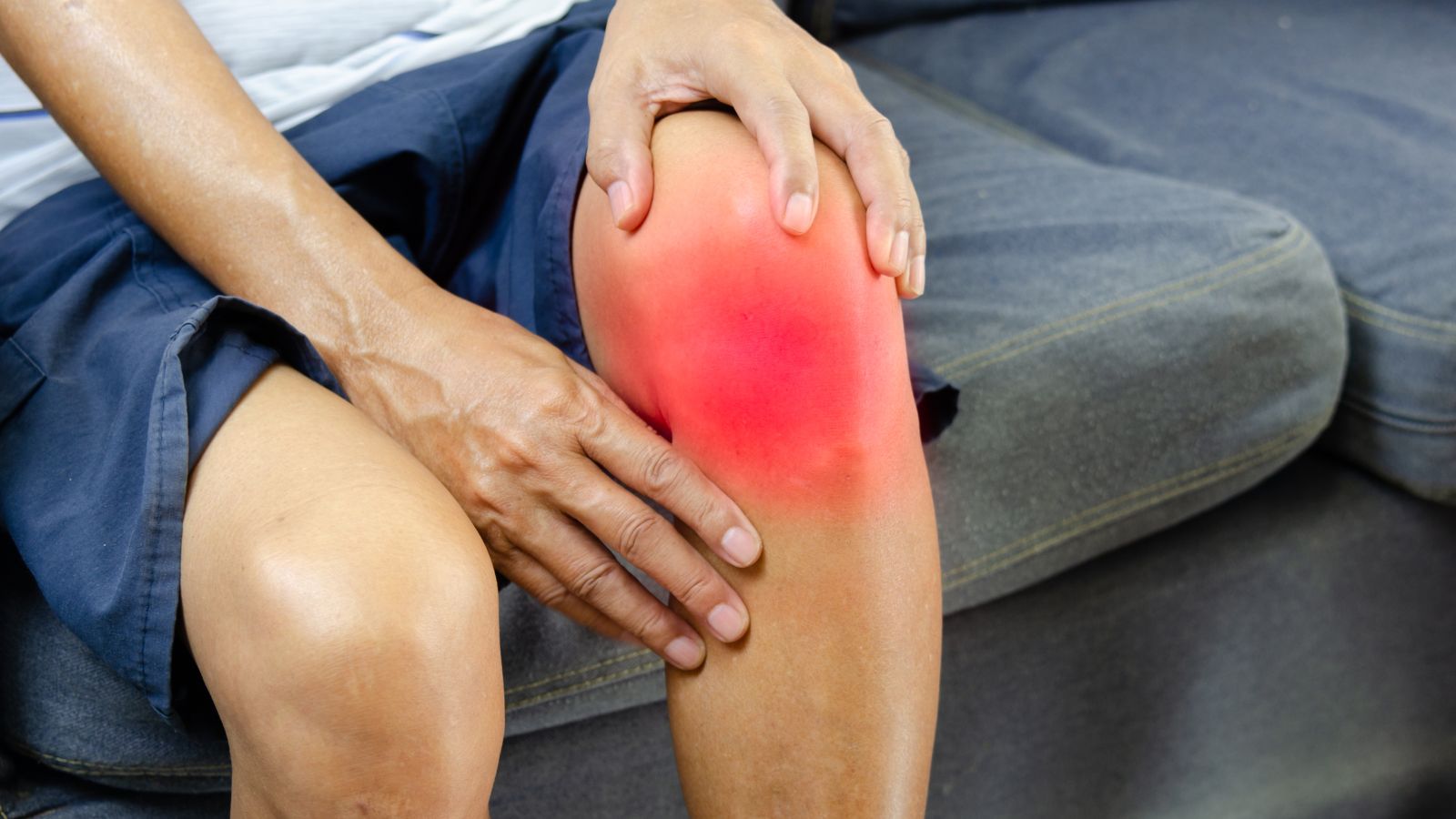
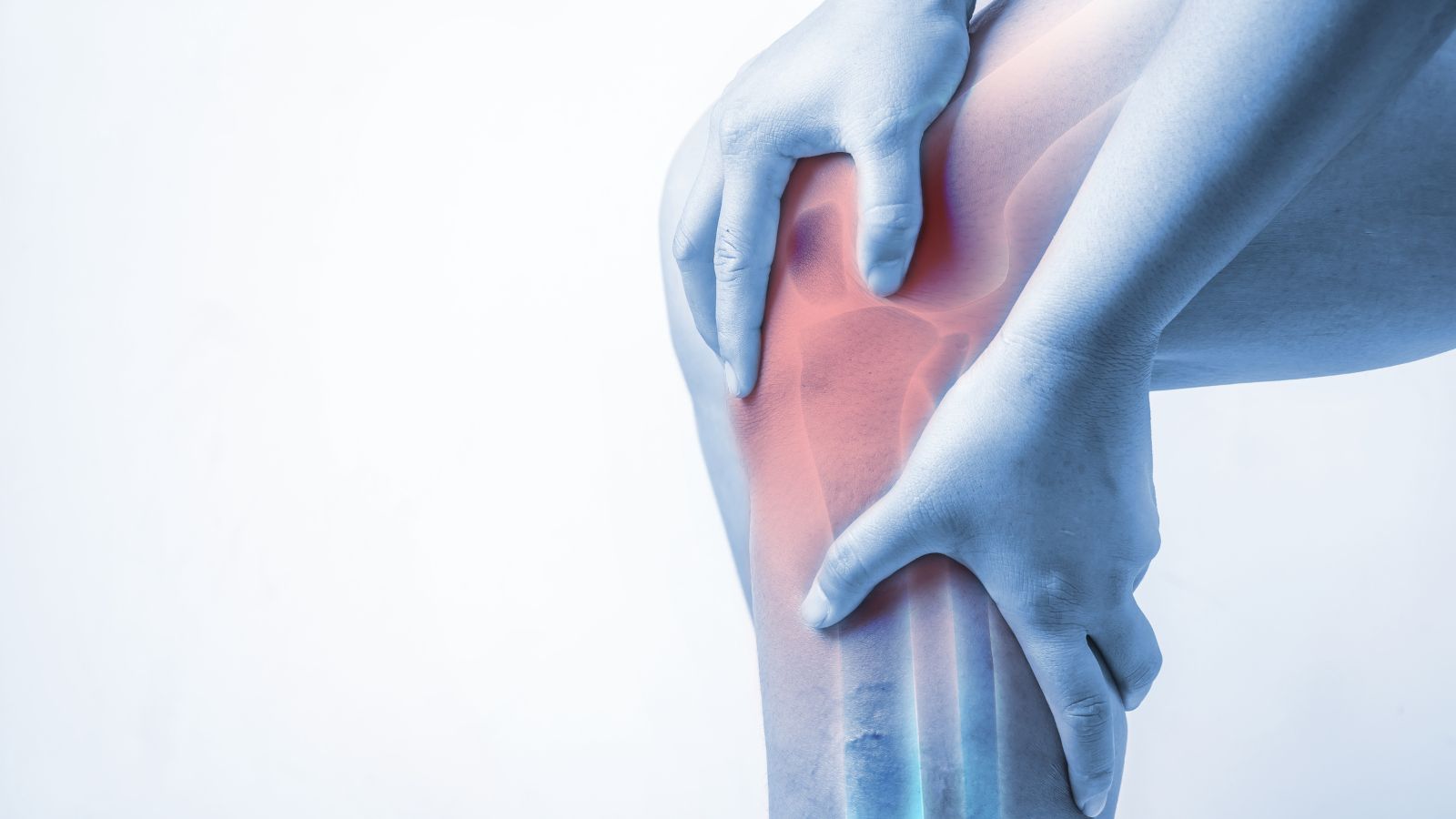
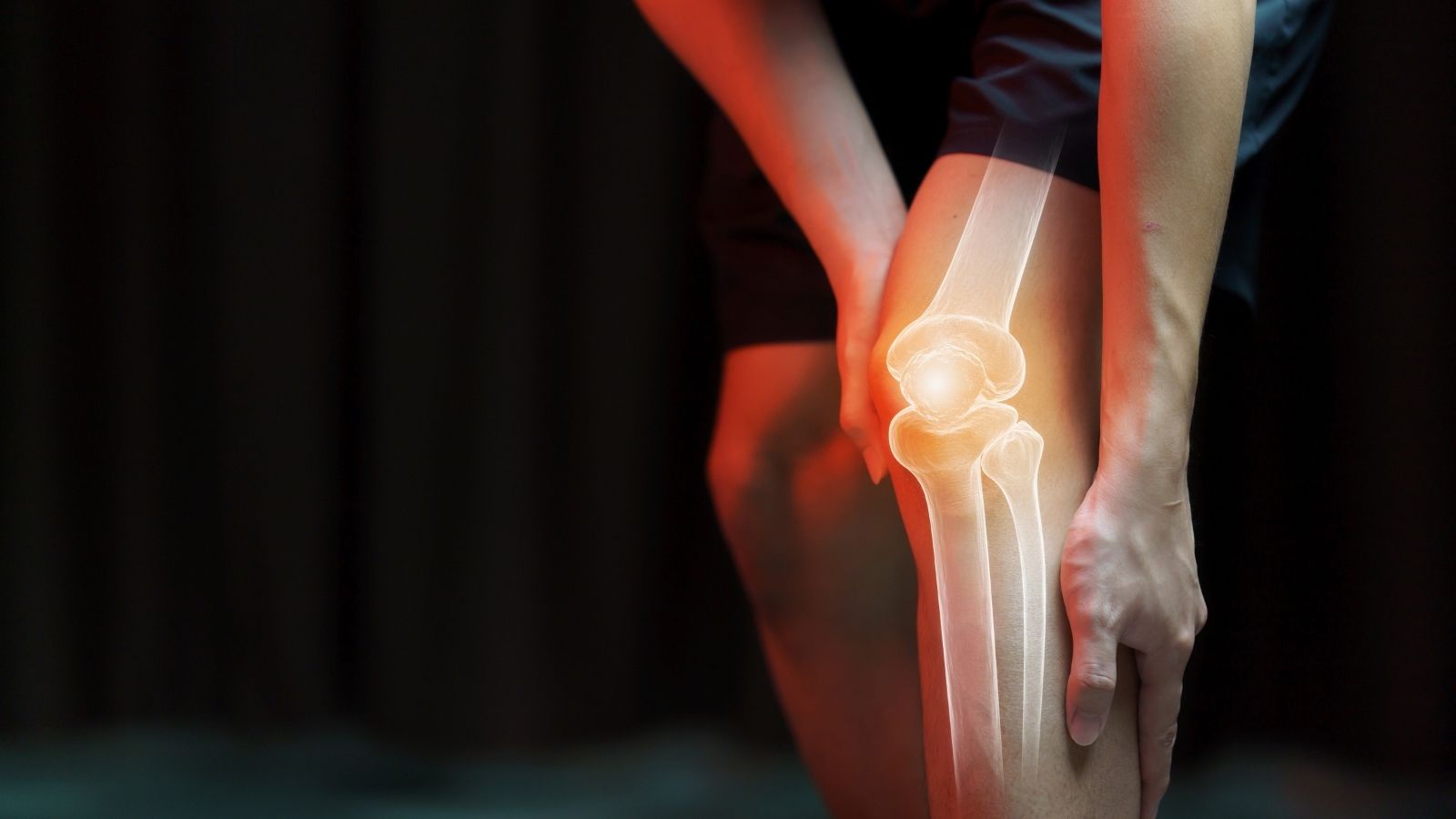
Knee disorders and pain develop as a result of damage to joint structures, cartilage wear, or ligament injuries. The knee joint, which is frequently used in daily life, is sensitive to trauma and degenerative diseases. Pain, limited mobility, and swelling are among the most common symptoms.
Causes of knee pain include meniscus tears, anterior cruciate ligament injuries, osteoarthritis, and rheumatic diseases. These issues are common in both athletes and older individuals. Early diagnosis plays a critical role in slowing the progression of the condition.
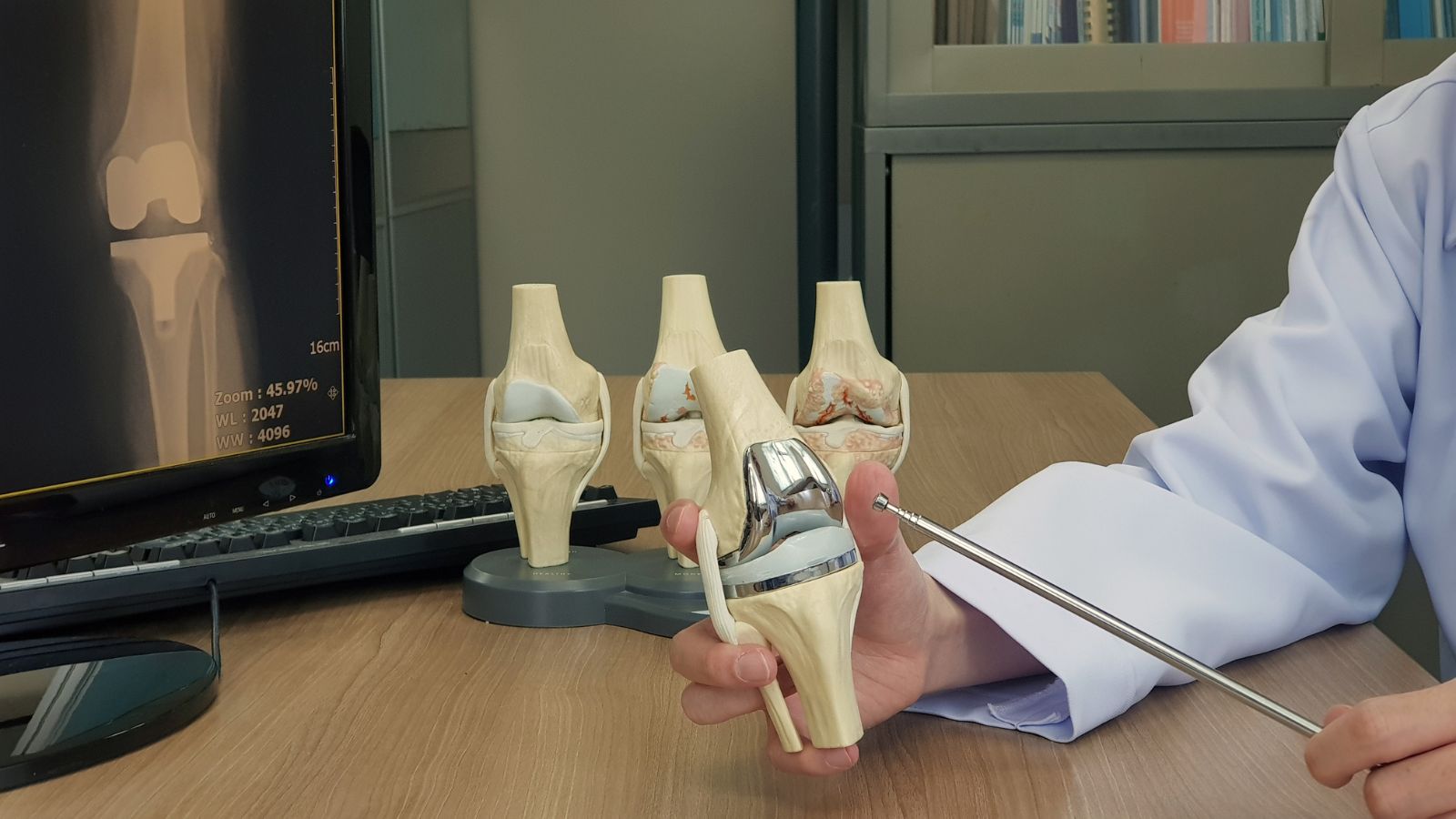
The diagnosis of knee disorders involves clinical examination, X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound. These tests allow detailed evaluation of the joint structures. Accurate diagnosis is essential for selecting the appropriate treatment method.
Treatment of knee pain includes medications, physical therapy, intra-articular injections, and surgical interventions. While conservative treatment is preferred for mild to moderate problems, arthroscopy or joint replacement surgery may be performed in cases of advanced cartilage damage or ligament ruptures.