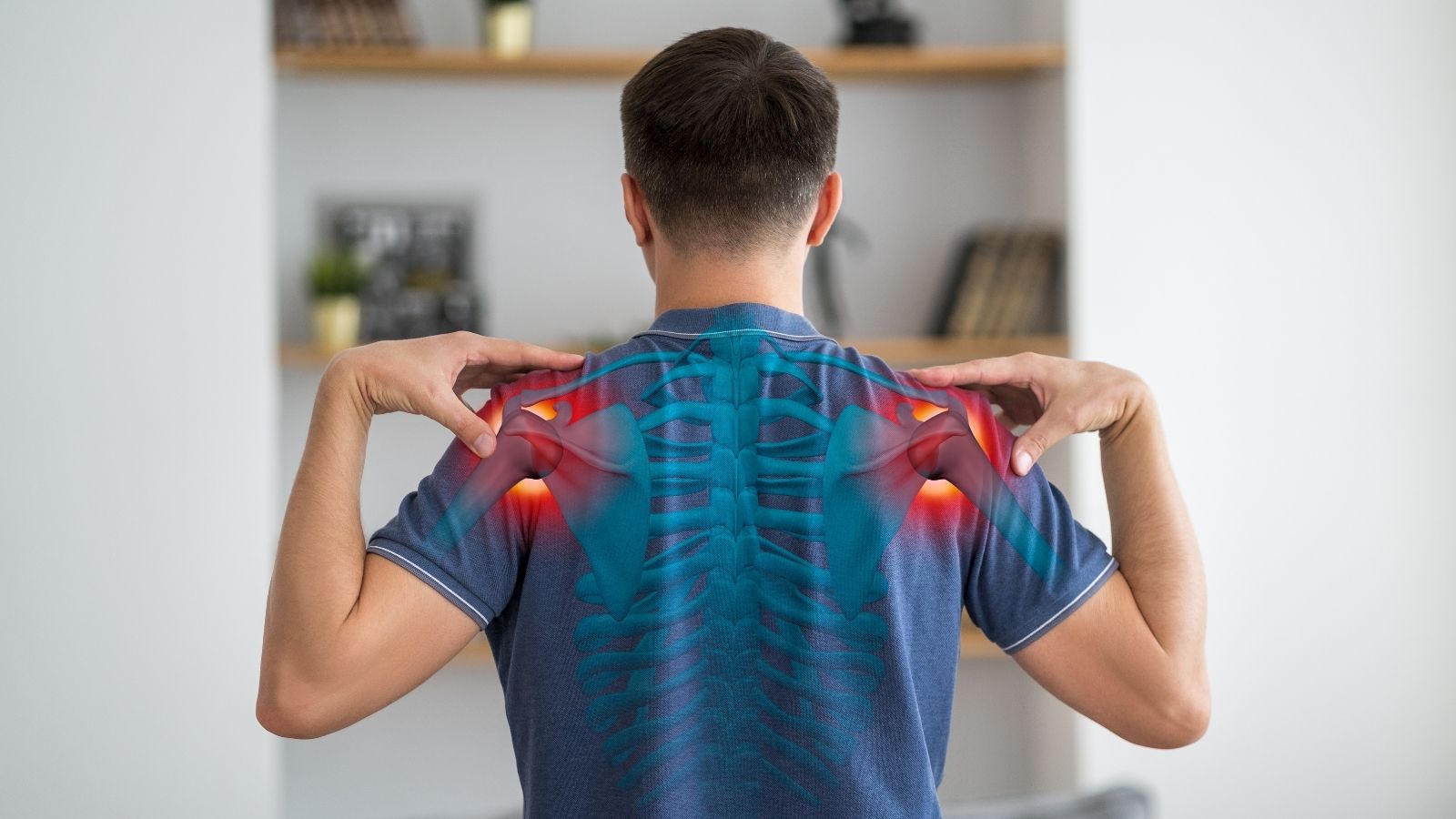
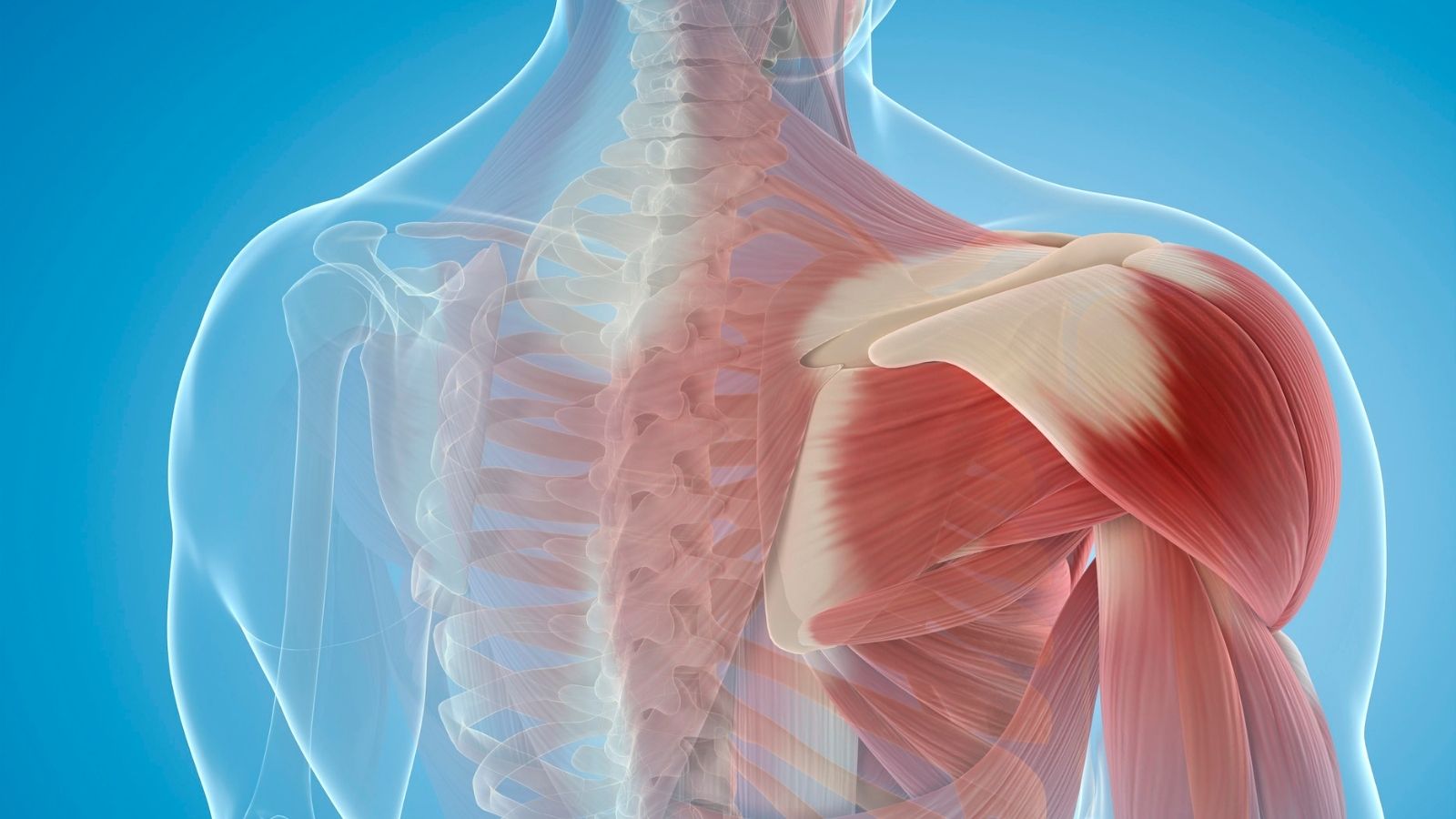
Shoulder disorders and pain arise from injuries or degenerative processes affecting the joint structures, muscles, and tendons. The most common causes include rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement syndrome, and osteoarthritis. Pain and limited range of motion are the primary symptoms.
Causes of shoulder pain include repetitive strain, trauma, rheumatic diseases, and age-related cartilage wear. These conditions negatively affect daily activities, particularly lifting the arm and carrying loads. Early intervention improves treatment outcomes.
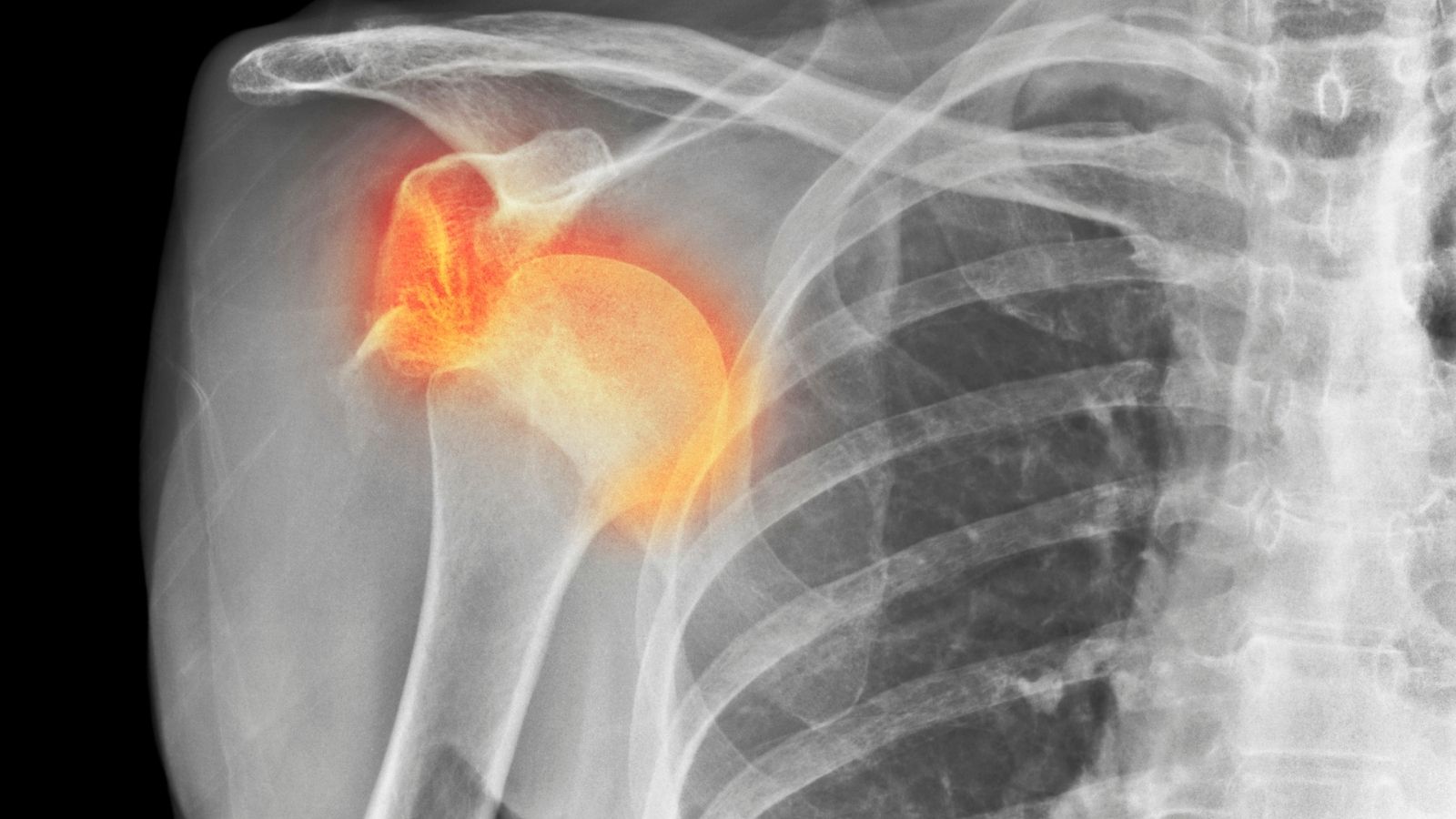
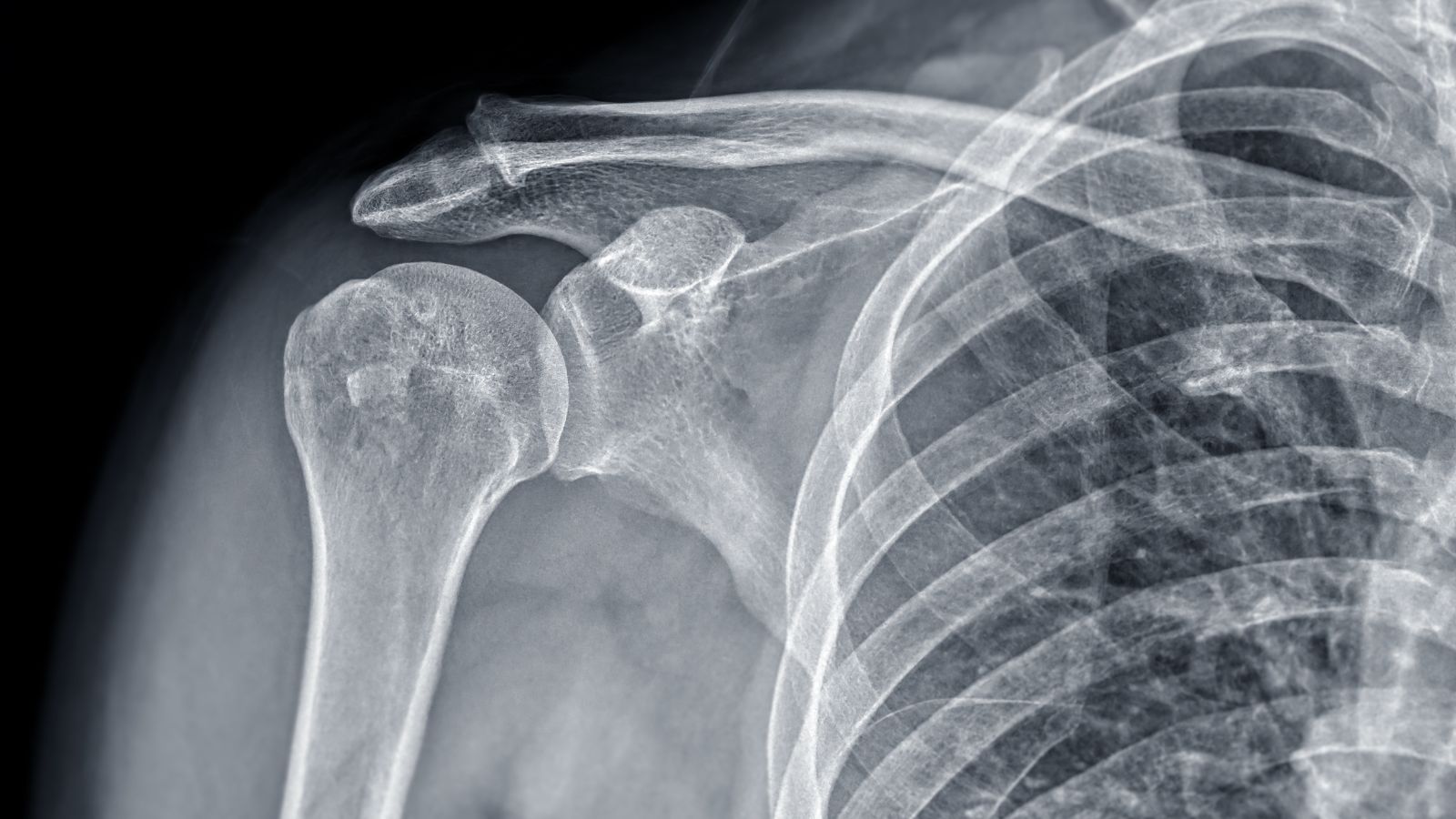
The diagnosis of shoulder disorders involves physical examination along with ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and X-ray. These methods allow detailed evaluation of tendon, muscle, and joint structures. Accurate diagnosis ensures the selection of an appropriate treatment according to the stage of the disease.
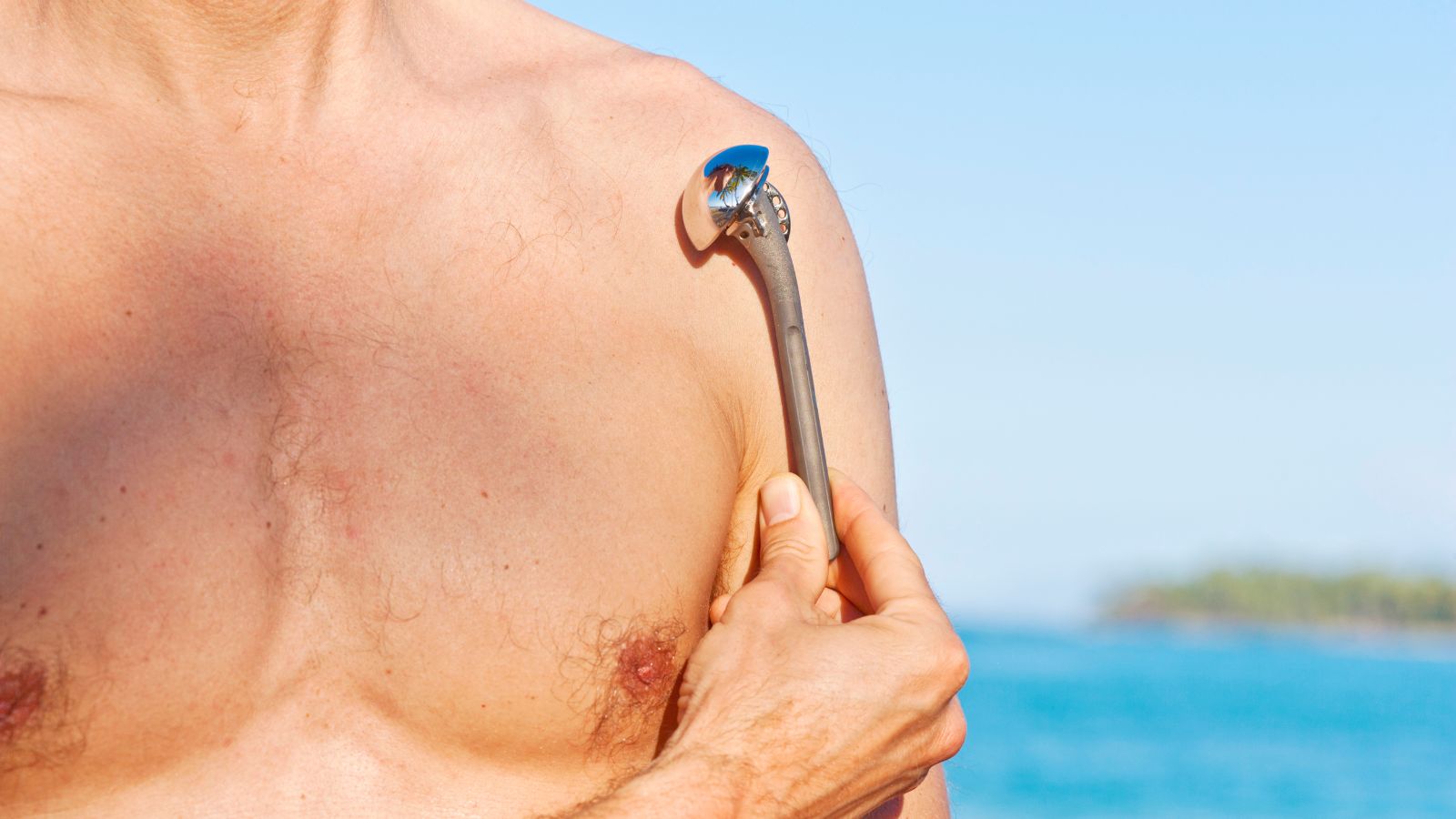
Treatment of shoulder pain includes rest, medication, physical therapy applications, injections, and surgical methods. While conservative approaches are preferred in mild cases, arthroscopic surgery may be performed in advanced tendon tears or significant joint damage.