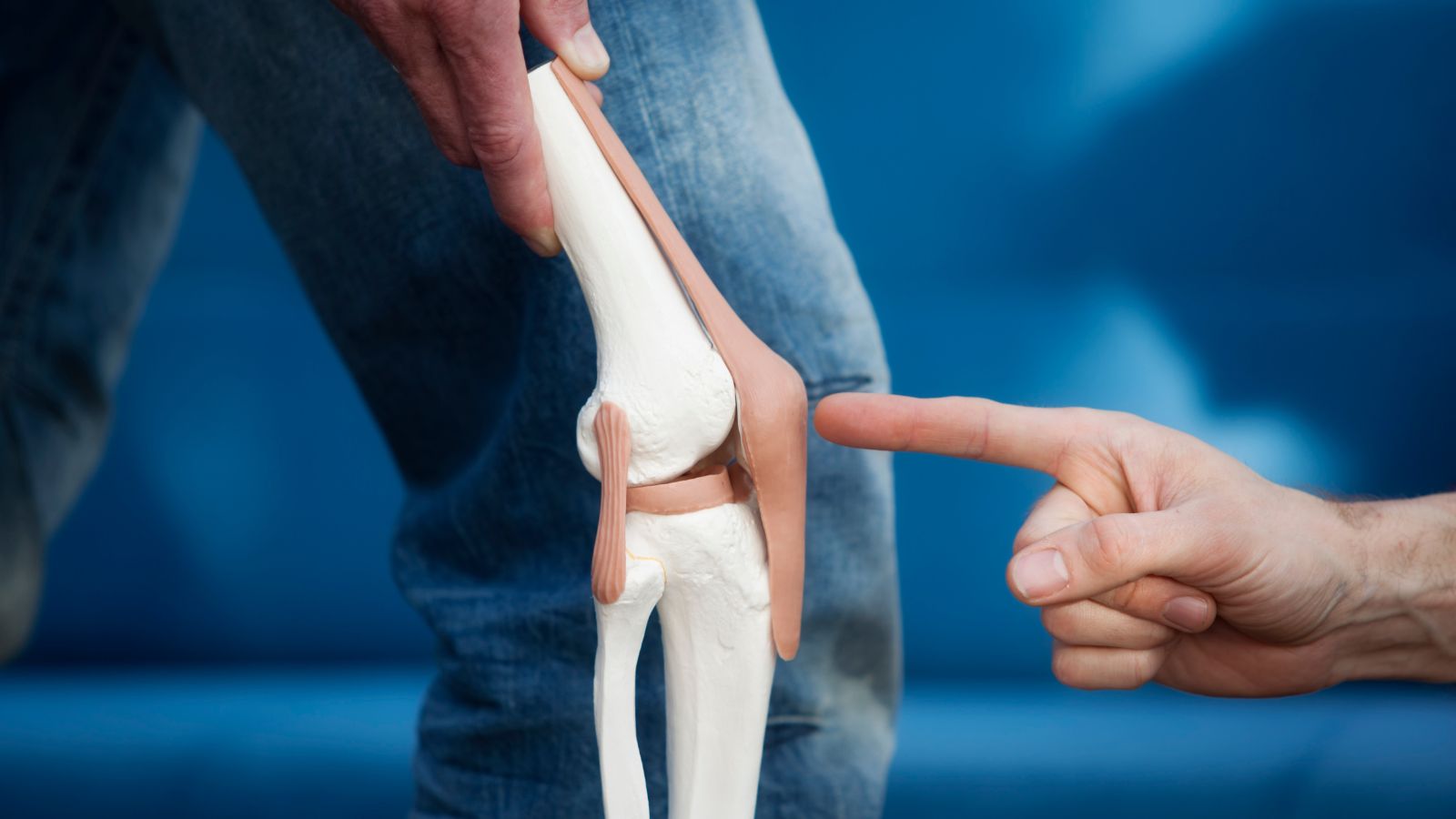
Prof. Dr. Murat Demirel, one of the best orthopedic doctors performing robotic knee replacement surgery in Ankara, stands out with his expertise in restoring knee joint health through advanced technology-supported surgical methods. Robotic knee replacement surgery is a modern method performed using computer-assisted systems and robotic surgical devices, allowing the implant to be placed with millimetric precision. Thanks to this technology, postoperative joint alignment, mobility, and the longevity of the prosthesis are significantly improved. In hospitals in Ankara where robotic knee replacement surgeries are performed, Prof. Dr. Demirel applies personalized surgical plans in centers equipped with advanced medical technology and high hygiene standards.
By conducting detailed evaluations and 3D joint modeling before surgery, Prof. Dr. Demirel ensures the selection of the most suitable prosthesis and closely follows up with his patients after the procedure. With his medical recommendations, the recovery process after robotic knee replacement surgery progresses quickly, safely, and comfortably. Additionally, he provides transparent and up-to-date information about robotic knee replacement surgery costs in Ankara, helping patients make informed decisions. You can also schedule an appointment immediately to regain your knee health, achieve pain-free freedom of movement, and improve your quality of life.
| Surgery Name | Robotic Knee Replacement (Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty) |
| Application Area | Knee joint (femur, tibia, patella joint surfaces) |
| Indications | Advanced osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, prosthesis planning for deformed knees |
| Surgical Method | Open surgery with computer and robot-assisted precise implant placement |
| Type of Anesthesia | Spinal, epidural, or general anesthesia |
| Operation Duration | Approximately 2–2.5 hours (may be slightly longer than conventional surgery due to planning and alignment process) |
| Hospital Stay | Usually 3–5 days |
| Recovery Period | 6–12 weeks; early mobilization and physical therapy are recommended |
| Complications | Infection, implant loosening, knee stiffness, nerve-vessel injury |
| Advantages | More precise bone cuts, optimal implant alignment, potentially longer-lasting results, shorter recovery time |
| Alternative Methods | Conventional (manual) total knee replacement, partial knee replacement |
| Suitable Patient Profile | Patients with knee deformities requiring high precision, individuals with advanced osteoarthritis, patients with an active lifestyle |


Prof. Dr. Murat Demirel
Orthopedics and Traumatology Specialist
Orthopedics Specialist Prof. Dr. Murat Demirel was born in Ankara in 1974. He completed his primary education at Ankara Kavaklıdere Primary School and his secondary and high school education at Ankara Atatürk Anatolian High School. Dr. Demirel graduated from Ankara University Faculty of Medicine in 1998 and completed his residency in Orthopedics and Traumatology at Ankara Numune Training and Research Hospital, 1st Orthopedics and Traumatology Clinic, in 2004.
PhD
Ankara University Institute of Health Sciences
Specialization
Ankara Numune Training and Research Hospital, 1st Orthopedics Clinic
Medical School
Ankara University Faculty of Medicine
Yazı İçeriği
What is Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery and Does the Surgeon’s Role Change?
I understand the greatest curiosity and concern on this subject. When people hear the word “robotic,” many imagine an autonomous machine performing the surgery on its own, like in the movies. Let’s correct this misconception right away: a robot does not perform the knee replacement surgery. The operation is carried out from start to finish by an experienced orthopedic and traumatology specialist with all their knowledge, experience, and decision-making skills.
So, what is the role of the robot here? You can think of the robotic system as an extension of the surgeon’s hand and eye. It is an extremely advanced assistant that combines the surgeon’s expertise with the millimetric precision of an engineer. This system allows the surgeon to transfer the perfect plan in their mind to the surgical field with zero error. What lies on the operating table is not a patient left to a machine, but a patient under the care of a skilled surgeon supported by the highest level of precision technology. In other words, the surgeon’s role does not change; rather, it becomes stronger and more precise. Simply put, the captain is still the surgeon; the robotic system is the most advanced navigation system guiding the ship safely and accurately to its destination.
This technology works on a three-dimensional (3D) virtual model of the patient’s anatomy created before the surgery. The surgeon plans all cuts, the implant size, and placement on this model in detail before entering the operating room. During the operation, the robotic arm guides the surgeon, ensuring strict adherence to this plan. The goal is to achieve the perfect balance and alignment unique to each patient.
What are the Main Differences Between the Traditional Method and Robotic Knee Replacement?
Traditional knee replacement surgeries have given millions of people a pain-free life for decades and are a proven method of success. Robotic surgery takes this proven success one step further with technological precision. The differences between traditional and robotic approaches can be summarized under a few main headings:
- Preoperative Planning
- Intraoperative Precision
- Soft Tissue Balance and Protection
- Level of Personalization
Let’s elaborate on these points. In the traditional method, surgical planning is generally based on two-dimensional standard X-rays. This is like a tailor using a standard pattern to sew a suit; the results are usually good but may not fit every body perfectly. In robotic knee replacement, the situation is completely different. With preoperative computed tomography (CT), a three-dimensional copy of the patient’s knee is created. This is like a tailor taking your exact measurements and preparing a custom pattern. On this 3D model, the surgeon evaluates the bone structure, the extent of cartilage wear, and the load-bearing axis of the leg from every angle. The ideal implant size, the exact angle and depth of bone cuts are planned flawlessly in a virtual environment before the surgery begins.
The intraoperative precision may be the greatest difference. In the traditional method, the surgeon makes bone cuts using their experience and hand skills with the help of special guides. In robotic surgery, however, the surgeon operates with a robotic arm locked into the 3D plan. This arm has a “virtual wall” or “haptic feedback” system that prevents the surgeon from going even a millimeter outside the planned cutting area. If the instrument approaches the boundary of the planned cut, the system either warns the surgeon or stops the tool at that point. This invisible force field ensures not only the perfect execution of bone cuts but also, most importantly, the protection of surrounding healthy bone, blood vessels, nerves, and muscles from unwanted contact.
This precise work means better protection of soft tissues, such as muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The success of knee replacement depends not only on proper bone alignment but also on the perfect balance of these soft tissues. Robotic systems can dynamically measure ligament tension during movement and provide numerical data to the surgeon. As a result, the knee feels more natural and balanced during movement. In short, robotic knee replacement transforms surgery from a standard procedure into a personalized art form, offering each patient a tailor-made solution.
Who are Good Candidates for Robotic Knee Replacement?
Whether this surgery is the right choice for you is something we decide together after a detailed consultation and evaluation. This is a highly personal decision. However, there are some common conditions and complaints that usually lead patients to consider knee replacement surgery.
The common complaints that typically bring patients to us for knee replacement are:
- Persistent pain that does not go away even at rest
- Severe pain that wakes you up at night
- Difficulty climbing stairs or walking uphill
- A significant decrease in walking distance over time
- Noticeable deformity or misalignment in the knee
- Instability, “giving way,” or “locking” sensation in the knee
The most common underlying cause of these complaints is osteoarthritis, commonly known as “wear and tear arthritis.” This occurs as the cartilage in the joint wears down over time. Another frequent cause is rheumatoid arthritis, an inflammatory disease where the body’s immune system attacks its own joints. Post-traumatic arthritis, which develops after a previous fracture or ligament injury, may also necessitate knee replacement.
Knee replacement is generally considered a last resort. In other words, before considering this surgery, all other non-surgical treatment options must have been tried without adequate relief. If medications, physical therapy, weight loss, or intra-articular injections are no longer effective in relieving your pain and your quality of life is severely impaired, robotic knee replacement may be a life-changing solution. In principle, every patient suitable for traditional knee replacement is also a candidate for robotic knee replacement. Particularly in patients with significant deformities or complex anatomy, the planning and precision provided by robotic systems increase the chances of success even more.
What are the Possible Advantages of Robotic Knee Replacement?
The superior precision that robotic technology brings to surgery can translate into tangible, everyday benefits for our patients.
Some key advantages of robotic surgery are:
- More accurate and precise implant placement
- A more natural joint feel
- Less damage to surrounding soft tissues
- Less pain and swelling after surgery
- Potentially faster recovery process
- Generally shorter hospital stay
- Potentially longer implant lifespan
These advantages are interconnected like links in a chain. The precise, patient-specific placement of your implant ensures the perfect restoration of your body’s weight-bearing axis. This means balanced load distribution on the implant. As a result, you feel smoother and more natural movement when bending, walking, or running.
Causing less trauma to surrounding muscles, ligaments, and tendons during surgery makes the postoperative period more comfortable. Less tissue damage usually means less pain, swelling, and bruising. This allows you to get back on your feet sooner, perform your physical therapy exercises more easily, and return home from the hospital faster. Many patients can be safely discharged within one or two days after surgery. When all these positive effects come together, the best possible environment is created for your implant to integrate with the bone and serve you for many years without problems.
As with Any Technology, Are There Risks in Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery?
In medicine, there is never a 100% guarantee, and every surgical procedure carries potential risks. Being transparent and discussing these openly is the foundation of a healthy doctor-patient relationship and informed decision-making. First, it should be emphasized that the general surgical risks present in all knee replacement surgeries—such as infection, deep vein thrombosis (blood clot in the leg veins), anesthesia-related complications—also apply to robotic surgery. Robotic technology does not eliminate these fundamental risks but may help manage them.
Some situations that can be considered specific to robotic surgery are:
- Slightly longer surgery duration
- Need for preoperative computed tomography
- Very rare risks associated with navigation pins
- Possibility of technical system issues
- Higher initial cost
Due to additional steps such as setup of the robotic system in the operating room, calibration, and introducing the patient’s anatomy into the system, the total duration of the surgery may be slightly longer (usually 15–20 minutes) compared to the traditional method. As the surgeon and team gain more experience, this time difference nearly disappears.
Most robotic systems require a preoperative computed tomography (CT) scan to create that perfect 3D plan. With modern CT devices today, the radiation exposure during this process is quite low, but it should still be noted that there is radiation exposure.
During surgery, in order for the robotic system to track the position of your leg, small metal pins (markers) are placed into the thigh and shin bones through tiny incisions. At these entry points, although extremely rare, complications such as infection, nerve sensitivity, or a small fracture may occur.
As with any advanced technological device, there is a theoretical possibility of a software or hardware malfunction during surgery. This is extremely rare, and experienced surgical teams are always prepared to continue the operation with the traditional method if such a situation arises.
Finally, the issue of “robotic knee surgery costs” or “robotic knee replacement surgery costs” is also an important factor. The technology itself, its maintenance, and the special single-use materials required for each surgery can increase the total cost compared to the traditional method. This is a disadvantage that should be taken into consideration.
How Does the Recovery Process Progress After Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery?
Just as the success of the surgery depends on the surgeon and technology, the success of recovery equally depends on you and your commitment to the rehabilitation process. This is a journey requiring mutual effort.
First 24–48 Hours: After surgery, usually on the same evening or the next morning, you get up and take your first steps with the help of a physiotherapist. Early mobilization is very important to increase blood circulation, reduce clot risk, and preserve muscle strength. During this period, pain control is effectively achieved through modern anesthesia techniques and medications.
First Few Weeks: After being discharged from the hospital, a personalized rehabilitation program begins at home or in a physical therapy center. Initially, you may use a walker or crutches. At this stage, the focus is on regaining full extension (straightening) and adequate flexion (bending) of the knee, controlling swelling, and strengthening the leg muscles, especially the quadriceps on the front of the thigh.
1–3 Months: During this period, you typically stop using a walker or crutches and begin walking without support. Your mobility and confidence increase significantly. By the end of this period, most patients, with their surgeon’s approval, can return to daily activities such as driving.
3 Months and Beyond: This is the period when most of your life returns to normal. Your muscle strength and endurance continue to improve. At this stage, to maximize the lifespan of your implant, it is best to choose joint-friendly activities rather than high-impact sports. Full recovery and achieving the maximum potential of your knee may take 6 months to a year. Patience and adherence to the exercise program are very important during this process. Reviews from patients who have undergone robotic knee replacement surgery show that the most satisfied patients are those who take the rehabilitation process seriously and strictly follow their doctor’s recommendations.
Some low-impact activities you can safely return to after surgery include:
- Swimming
- Water exercises
- Stationary or regular cycling
- Brisk walking on flat ground
- Golf
- Couple dancing (such as Tango, Waltz)
- Pilates or yoga (with modified movements)
Contact us for detailed information and an appointment!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is robotic knee replacement surgery?
Robotic knee replacement surgery is a surgical procedure in which the knee joint, when severely damaged, is replaced with an artificial joint. In this surgery, robotic surgical systems are used to place the implant more precisely and in a patient-specific manner.
What advantages does robotic knee replacement surgery offer compared to the traditional method?
With robotic surgery, bone cuts are made with millimetric precision, the implant is placed much more accurately, and postoperative joint mobility and patient satisfaction increase. The risk of tissue damage is reduced, and the recovery process is shorter.
Who is suitable for robotic knee replacement surgery?
It is generally suitable for older patients experiencing pain and movement limitations due to osteoarthritis, who have not responded to medication or physical therapy. Robotic surgery may be particularly preferred in patients with abnormal knee anatomy or those who have had previous knee surgery.
How is the surgery performed and how long does it take?
First, three-dimensional images of the patient’s knee are taken. The robotic system guides the surgeon during surgery and ensures high precision while making cuts. The duration of surgery is similar to the traditional method and usually ranges between 1–2 hours.
What is the recovery process like after surgery?
Most patients are mobilized on the same day or the next day after surgery. The hospital stay is usually 2–4 days. With physiotherapy programs and exercises, joint mobility is quickly regained in the first few weeks. Full recovery usually takes 6–12 weeks.
What are the risks of robotic knee replacement surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, there may be risks such as infection, blood clotting, nerve or vessel injury, and implant loosening. However, robotic surgery minimizes these risks, and complication rates are very low.
Will there be pain after robotic knee replacement surgery?
Mild to moderate pain after surgery is normal. Pain can be controlled with modern surgical techniques and painkillers. Since robotic surgery causes less damage to soft tissues, pain is generally less intense.
What is the lifespan of a robotic knee implant?
The lifespan of implants placed with robotic surgery is generally 15–20 years. The implant’s longevity depends on the patient’s age, weight, activity level, and postoperative care.
Is robotic knee replacement surgery performed in public hospitals?
In Turkey, robotic knee replacement surgery can be performed in some state hospitals in major cities. However, it is mostly used in private hospitals and specialized centers. Whether the surgery is covered by insurance and its cost may vary depending on the hospital.
Can sports be done after robotic knee replacement surgery?
After surgery, light exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling may be started as recommended by the doctor. However, high-risk sports involving sudden or heavy joint stress should be avoided. It is important to consult your doctor before returning to sports activities.